

Ever wondered how THCa flower is grown? Growing THCA-dominant hemp flowers while keeping delta-9 THC levels under the federal legal limit is a complex and intricate process.
In the United States, the 2018 Farm Bill enables this endeavor, supported by special genetics and cultivation techniques.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the steps and strategies involved in successfully growing THCA-dominant hemp flowers within the constraints of the law.
The Hemp Farm Bill and its Impact on How THCa Flower is Grown
The Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018, commonly known as the 2018 Farm Bill, played a pivotal role in the cultivation and regulation of hemp, including THCA-dominant varieties.

The Farm Bill removed hemp from the list of controlled substances and redefined it as a legal agricultural crop, provided that it contains less than 0.3% delta-9 THC on a dry weight basis.
This shift in legal status opened up new opportunities for farmers and researchers interested in developing and growing THCA-rich hemp varieties.
Defining THCA and Delta-9 THC
To better understand THCA flower cultivation and the legal limits, it’s essential to distinguish between two key components: THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and delta-9 THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol).

THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to delta-9 THC, meaning it does not produce the intoxicating effects associated with marijuana. Delta-9 THC, on the other hand, is the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” associated with cannabis.
While THCA is not psychoactive, its concentration can be used to indicate the potential for delta-9 THC production once the plant is heated or decarboxylated.

Legal Limits for Delta-9 THC
Under the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp is defined as cannabis with a delta-9 THC concentration of 0.3% or less on a dry weight basis.
This distinction is crucial for growers because exceeding this limit could lead to the crop being classified as marijuana, which remains illegal at the federal level in the United States.
Therefore, one of the primary objectives of cultivating THCA-dominant hemp flowers is to ensure that the delta-9 THC levels remain below this threshold.

Special Genetics for THCA-Dominant Hemp
The success of THCA-dominant hemp cultivation begins with selecting the right genetics. To achieve a higher THCA content and lower delta-9 THC levels, growers often turn to specially bred hemp varieties.
These varieties are typically developed through selective breeding techniques, emphasizing specific traits and cannabinoid profiles.
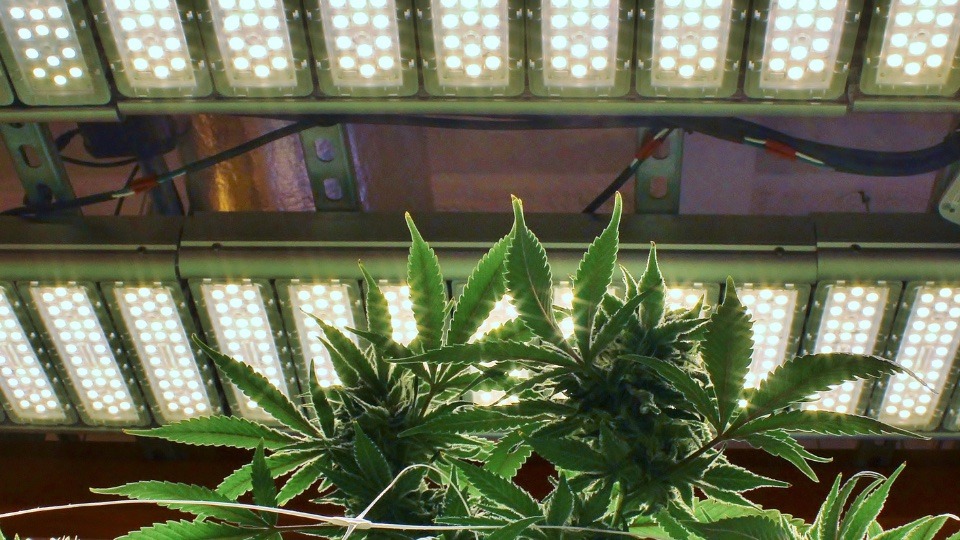

Breeding for High THCA Content
Breeding for high THCA content involves selecting parent plants with elevated THCA production. These parent plants may have naturally occurring genetic traits that favor THCA over delta-9 THC.
Over successive generations, breeders can stabilize these traits to create hemp varieties with consistently high THCA content.
Wondering if THCa is natural? If yes, then click here.

Reducing Delta-9 THC
At the same time, breeders are actively working to decrease the activity of the gene responsible for producing delta-9 THC. Essentially, they’re focusing on minimizing the part of the plant’s genetic code that leads to the formation of delta-9 THC.
This effort reflects a broader goal of developing cannabis varieties that have lower levels of the psychoactive compound, aligning with preferences for products that offer therapeutic benefits without the intense ‘high’ associated with higher THC strains
Genetic selection, utilizing advanced techniques like marker-assisted breeding, identifies plants with lower delta-9 THC potential. The goal is to create strains that are rich in THCA but contain minimal delta-9 THC.
Cloning and Tissue Culture
In addition to traditional breeding methods, cloning and tissue culture techniques are employed to ensure the genetic stability of THCA-dominant hemp varieties.

Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mother plant that exhibits the desired traits, allowing growers to produce genetically identical offspring.
Tissue culture, a more advanced method, involves growing plant cells in a controlled environment to preserve genetic characteristics.

Cultivation Techniques to Maintain Legal Delta-9 THC Levels: How THCa is Grown Continued…
After securing the right genetics, growers use techniques to keep delta-9 THC below legal limits while maximizing THCA production.
Here are some strategies that farmers employ:
Harvest Timing
Harvest timing is a critical factor in delta-9 THC regulation. The longer hemp plants mature, the more time there is for THCA to convert into delta-9 THC.
To avoid this conversion, farmers often harvest their crops before full maturity, ensuring that the delta-9 THC levels remain within the legal limit.

Monitoring Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity play a significant role in cannabinoid production. By carefully controlling these factors, growers can influence the cannabinoid profile of their plants.
For THCA-dominant hemp, optimizing these conditions to favor THCA over delta-9 THC is vital.
Fertilization and Nutrient Management
Proper fertilization and nutrient management are crucial to achieving the desired cannabinoid profile. That all effects how THCa flower is grown. Balancing essential nutrients and avoiding excess nitrogen, which can encourage delta-9 THC production, is key to success.
Hemp cultivation often favors organic and sustainable nutrient management practices.

Genetic Stability
As mentioned earlier, maintaining genetic stability is essential to ensure that the plants consistently produce the desired cannabinoid profile.
This requires careful selection of mother plants for cloning and tissue culture and rigorous quality control in the propagation process.
Third-Party Testing
To ensure compliance with the legal delta-9 THC limits, it is common practice for hemp growers to conduct regular third-party testing of their crops.
Typically, a representative crop sample undergoes testing to confirm that it stays below the 0.3% delta-9 THC threshold

Challenges and Considerations
How is THCa flower grown? Well, that ultimately depends on a variety of complex factors.
While cultivating THCA-dominant hemp is legally feasible, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
Regulatory Variations
The legality of hemp cultivation varies from country to country and even within states in the United States. It’s crucial for growers to stay updated on the latest regulations and requirements in their specific region.

Risk of Non-Compliance
Maintaining delta-9 THC levels below the legal limit can be challenging, and there is always a risk of exceeding the threshold. Non-compliance can result in crop destruction, legal consequences, and financial losses.
Genetic Instability
Maintaining genetic stability in hemp strains can be a complex task. Breeders need to invest time and effort into preserving the desired traits in their selected varieties.

Market Demand
The market for THCA-dominant hemp products is likely to continue growing, driven by consumer interest in non-psychoactive cannabinoids and their potential therapeutic benefits.
Increased research on THCA and its effects will enhance consumer awareness, further boosting demand.
Market demand significantly shapes the cultivation of THCA flower. As consumer interest in legal cannabinoids rises, growers focus on genetics and techniques that deliver high THCA content while keeping delta-9 THC levels within legal limits.
Meeting this demand while complying with regulations is a pivotal challenge.

Addressing the Myth that it is Impossible to Keep THCa Genetics Under the Federally Permissible THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) Limit Unless You’re Growing Type 1 Fiber or Grain Genetics
The claim that it is impossible to keep THCa (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) genetics under the federally permissible D9 (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) limit unless you’re growing type 1 fiber or grain genetics is not accurate.
While it is true that different cannabis strains and genetics can influence the levels of cannabinoids produced, there are various aforementioned factors and cultivation practices that can be employed to control and manage THCa levels within legal limits.
Enjoying reading, “How is THCa Flower Grown?” If yes, click here to check out more of our latest insights.

It’s essential to recognize that the cultivation and regulation of cannabis are dynamic fields, subject to advancements and changes in technology and legislation.
While some strains may have higher THC genetic predispositions, careful cultivation and regulatory compliance can control THCa within legal limits.
Cultivation Insights: Unveiling the Process of How THCa Flower is Grown
In the following certificate of analysis, you can see the high THCa content, and low delta-9 THC listed in the cannabinoid profile of a strain with non-type 1 fiber or grain genetics:
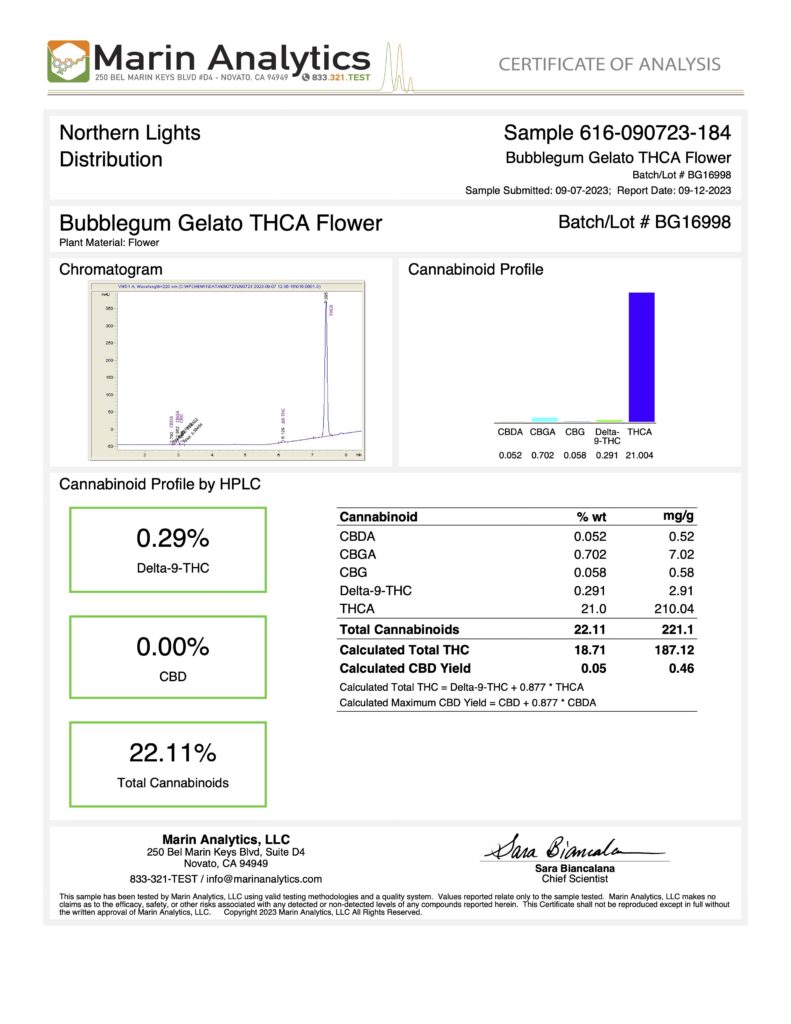
Crafting the sample analyzed in the lab test, as outlined in the Certificate of Analysis above, was a meticulous process that blended a myriad of factors and advanced cultivation practices.
The assertion that it is impossible to keep THCa genetics within federally permissible Delta-9 THC limits unless growing specific types of cannabis strains, such as type 1 fiber or grain genetics, oversimplifies a complex issue.

While various cannabis strains and genetics can influence cannabinoid levels, suggesting that only specific types are capable of meeting regulatory standards is an oversimplification.
The interaction between genetics and THC content holds significance, but it’s crucial to acknowledge that cultivators can actively employ various factors and cultivation practices to manage THCa levels responsibly.
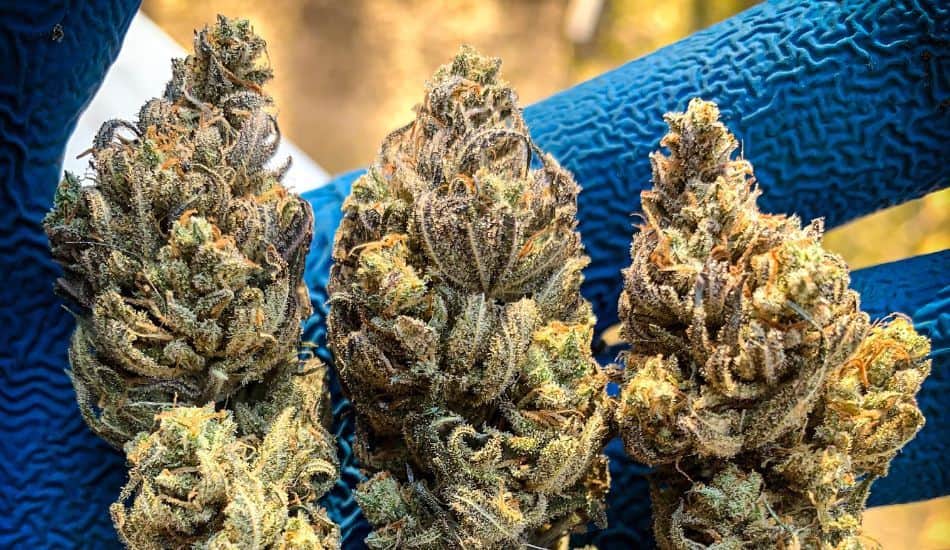

Pruning, light exposure, nutrient management, and harvest timing give cultivators tools to influence cannabinoid distribution in plants.
The dynamic nature of cannabis cultivation and regulation is crucial to understanding this issue. Ongoing advancements in technology, research, and legislation continually shape the landscape.
The claim underscores the need to adapt to changing circumstances, highlighting how evolving knowledge and techniques can now overcome past challenges.

Why People Tend to Oversimplify the Complexities of THC Regulation in Cannabis Genetics
People might oversimplify by associating specific genetic types with THC levels due to a lack of comprehensive understanding or misinformation. To debunk this claim, we present lab tests that showcase hemp or cannabis strains with non-type 1 fiber or grain genetics but still fall within federally permissible Delta-9 THC limits.
We demonstrate diverse strains that meet legal requirements, emphasizing that genetic diversity exists, and responsible cultivation practices play a crucial role in compliance.
This showcases the logical fallacy in the oversimplification, highlighting the multifaceted nature of THC regulation in different strains.
In the following certificate of analysis, you can see the high THCa content, and low delta-9 THC listed in the cannabinoid profile again, but in another distinct strain with non-type 1 fiber or grain genetics:
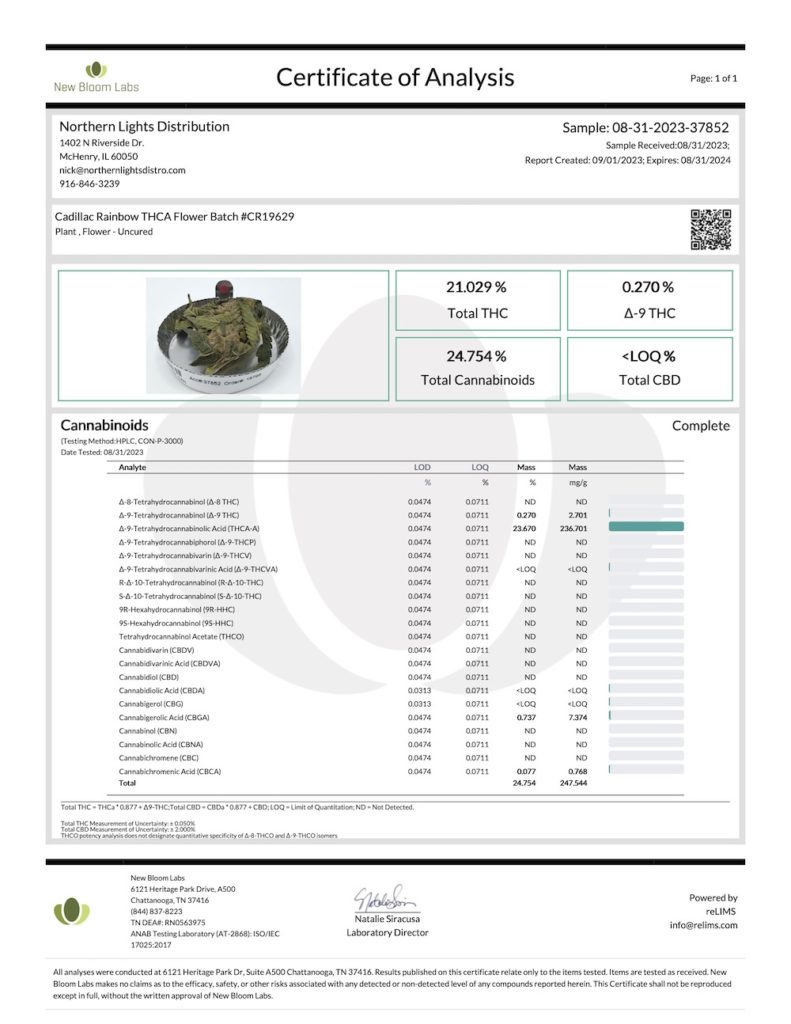
Showing multiple Certificates of Analysis (CoAs) for diverse strains can be an effective way to demonstrate that THC levels within federally permissible limits are not restricted to specific genetic types.
This approach provides a comprehensive view of the variety of strains that comply with regulatory standards, reinforcing the point that responsible cultivation practices, rather than specific genetic categories, are key in meeting legal requirements. It adds credibility to our argument and illustrates the diversity within the cannabis landscape.
Here is a 3rd party lab test taken of another distinct THCa-rich strain with non-type 1 fiber or grain genetics that is federally legal:
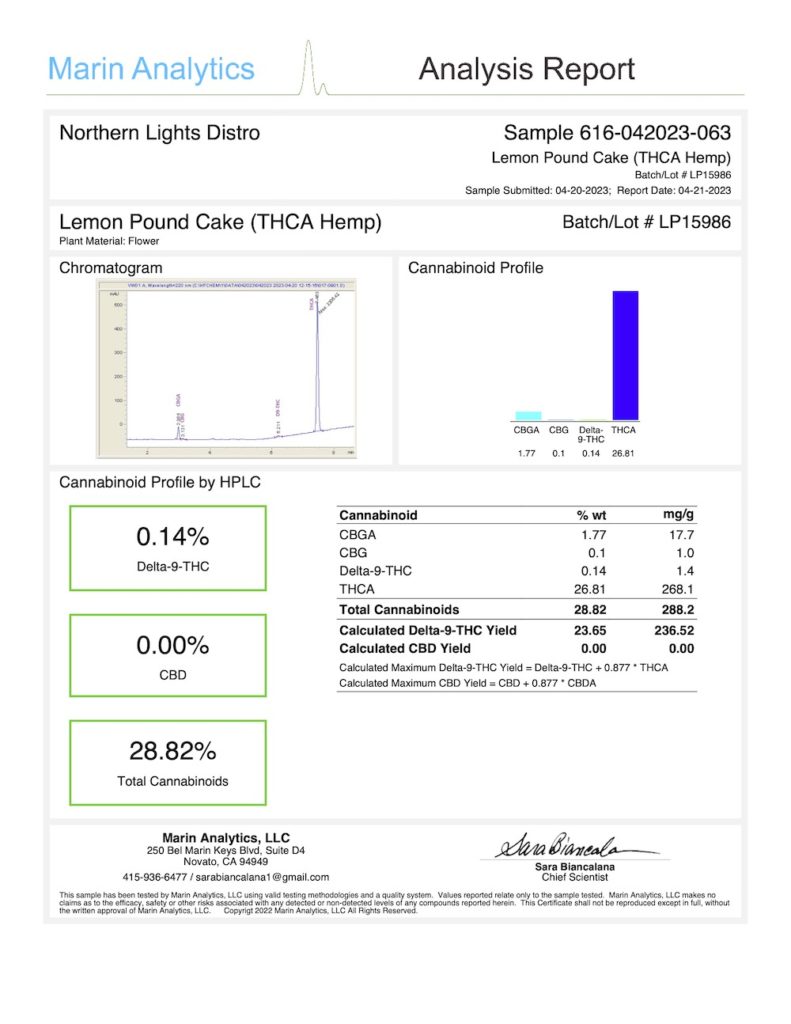
After examining this specific Certificate of Analysis, it becomes evident that adherence to federally permissible THC limits is not confined to a particular genetic category.
This strain, with its diverse genetic profile, underscores the nuanced nature of THC regulation. Responsible cultivation practices, as highlighted in this lab test, play a pivotal role in achieving compliance.
The Dynamic Nature of Cannabis Genetics
It’s crucial to recognize that the realm of cannabis genetics is dynamic, and diverse strains can thrive within legal limits.
Let’s continue exploring additional Certificates of Analysis to further solidify the understanding that THC content is a multifaceted interplay between genetics and cultivation practices.
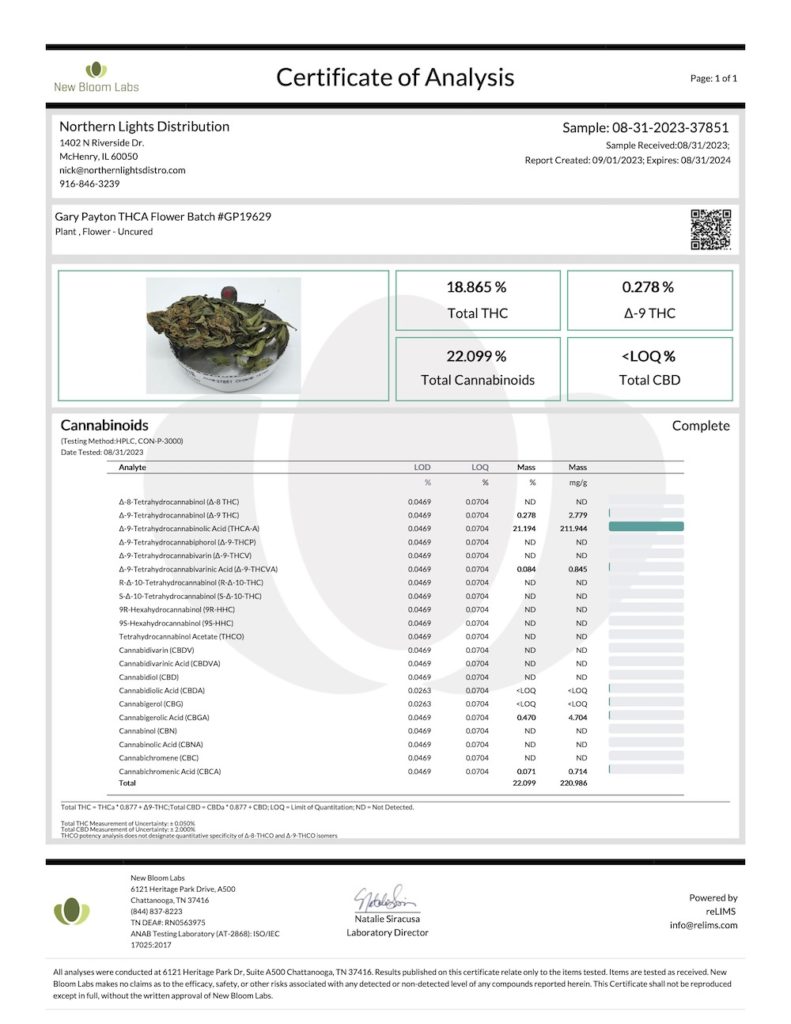

Each CoA presented reinforces the diversity of strains that adhere to federal THC limits, emphasizing the importance of cultivation practices in achieving compliance.

Adhering to regulations is crucial for responsible cultivation, requiring growers to stay informed and meet legal THC standards.
Some strains genetically predispose to higher THC, underscoring the need to grasp the nuanced interplay with genetics and THC levels.
Cultivators can control THCa levels within legal limits by using careful practices and staying informed on regulations. This challenges the idea that only specific strains meet these standards

Conclusion
Cultivating THCA-dominant hemp flowers while staying within federal THC limits is a fascinating challenge.
Thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp is no longer a controlled substance. Breeding and cultivation advances now enable exotic hemp varieties with high THCA content, meeting federal regulations.
Growers must carefully select genetics, monitor environmental factors, manage nutrients, and regularly test their crops to ensure compliance.
Despite challenges and risks, this endeavor opens avenues for farmers to enter the expanding market for hemp-derived products. Simultaneously, it grants consumers access to distinctive and beneficial cannabinoids without the psychoactive effects of delta-9 THC.
Alan Rachmann
Leave a Comment
About El Jay's
We take pride in offering organically-grown THCa flower that is lab-tested to ensure the highest quality and purity. Our dedication to using sustainable and natural growing practices ensures that our flower is free of harmful pesticides and chemicals. Click here to view all our product offerings.
Recent Posts
Shop Now
-
- Sale!
Wholesale THCa Hemp Live Resin Badder – Choose Your Strains
- $950.00 – $3,250.00Price range: $950.00 through $3,250.00
- Rated 5.00 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
El Jay’s THCa Hemp Diamonds
- $25.99 – $67.99Price range: $25.99 through $67.99
- Rated 4.80 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Contact Us
Sign up for our Newsletter
By submitting this form, you agree to receive emails from us.





